The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently widened its approval for the Nanox.ARC, a digital X-ray system that now includes its capacity for enhanced three-dimensional tomographic imaging. Initially sanctioned for musculoskeletal imaging, this platform, produced by Nanox, has now received clearance for a broader range of uses encompassing intra-abdominal, pulmonary, and paranasal applications.
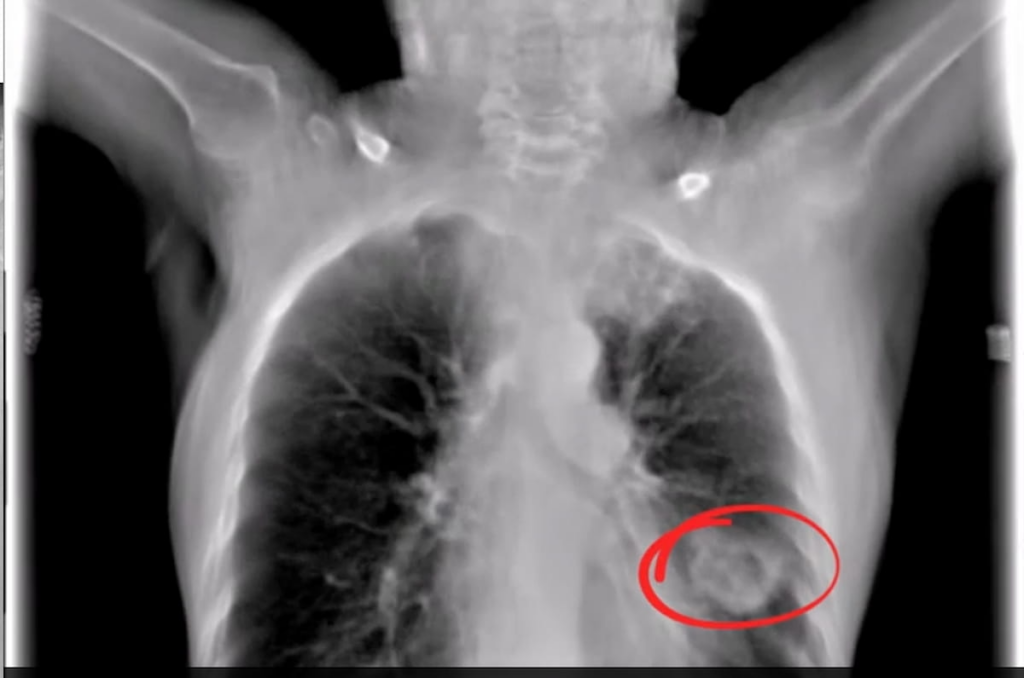
A significant feature of the Nanox.ARC system is its ability to reveal detailed imaging, as demonstrated with its digital tomosynthesis technology. For instance, in recent imaging, the system detected a distinct cavitational lesion as well as another encapsulated lesion located in the lower left lobe. Such imaging capabilities have led to the FDA’s expanded approval to include not only pulmonary imaging but also intra-abdominal and paranasal diagnostics.
What sets the Nanox.ARC apart is its integration of advanced tomosynthesis, which employs a cold cathode. This technology significantly mitigates the common issue of structure superimposition found in traditional X-ray systems. It instead offers three-dimensional visualizations by layering multiple images, allowing for more precise assessments.
Greg Kicska, M.D., Ph.D., who serves as an assistant professor at Harborview Medical Center in the Department of Radiology and is also part of the Nanox Advisory Board, notes, “When it comes to imaging the musculoskeletal system, the thoracic region, and the abdomen, digital tomosynthesis may provide advantages over CT scans or conventional radiography.” He points out that the Nanox system is distinguished not only by its superior image clarity but also by its efficiency; it is more compact compared to traditional X-ray machines, requires less power, and employs a unique matrix pattern. This pattern helps to minimize structural noise, thus producing clearer images.
The innovations found in the Nanox.ARC system open up new possibilities in medical imaging. Its ability to deliver high-quality, multi-layered images in a smaller, less power-intensive package makes it a valuable addition to the field. Such advancements reflect ongoing developments in imaging technology aimed at improving diagnostic capabilities while addressing the limitations of traditional X-ray systems.